INTRODUCTION
Skin and hair play a major role in a person’s appearance. The colour of human hair – such as black, brown, blonde etc. – depends on the type of melanin in human hair follicles and its transformation from melanocyte to keratinocyte i.e. melanogenesis[1]. As one grows older, melanocytes, the pigment cells in the hair follicles, die slowly; due to which, hair may not contain as much melanin as needed to maintain its color, and as a result, it turns grey, silver, or white. Greying of hair (also called canities) is no longer associated with age, and depends on several factors such as deficiency of vitamin B12[2], stress[3], smoking[4], genetics[5], and auto-immune diseases such as vitiligo and alopecia areata[6] etc. Reversal of greying of hair is now receiving the attention of researchers worldwide.
MECHANISM OF HAIR GREYING
The process of hair growth consists of 3 phases;
- Anagen, the active growth stage of the hair fiber
- Catagen, wherein hair growth slows down
- Telogen, wherein hair growth completely stops and the hair fiber falls off
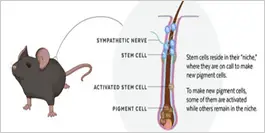
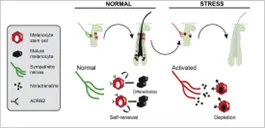
When hair is formed, melanocytes inject melanin into cells containing keratin, the basic structural protein of hair fibre, resulting in hair retaining its original colour[7]. Melanogenesis, a process of melanin production and distribution, is reported to be controlled by neuroendocrine factors such as alpha melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH),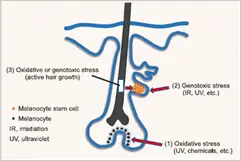 ß-endorphin, corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)], and micropthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF)[8]. Greying of hair is caused either by active hair growth; which induces oxidative or genotoxic stress in hair bulge, resulting in depletion of melanocyte stem cells (MSC); or dysfunction of melanocyte stem cells in the bulge, which in turn may be attributed to the generation of toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) on melanocyte nuclei and mitochondria[9].
ß-endorphin, corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)], and micropthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF)[8]. Greying of hair is caused either by active hair growth; which induces oxidative or genotoxic stress in hair bulge, resulting in depletion of melanocyte stem cells (MSC); or dysfunction of melanocyte stem cells in the bulge, which in turn may be attributed to the generation of toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) on melanocyte nuclei and mitochondria[9].

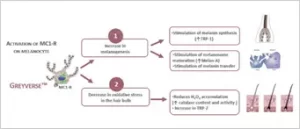 a skin condition that causes de-pigmentation of sections of skin[28]. An agonist of α‐melanocyte‐stimulating hormone (α‐MSH), a biomimetic peptide (palmitoyl tetrapeptide‐20, PTP20) was developed by Scalvino et al. and was found to enhance hair pigmentation, and retard hair-greying process[29]. Redenhair in Spain has developed Greyverse, which is an α-MSH analogue capable of binding to MC1-R, a transmembrane receptor located on the surface of the melanocytes and causing stimulation of melanogenesis process. It reduces the accumulation of H2O2 responsible for accelerating the grey hair formation process[30]. Experimental results showed that only 0.5% of Greyverse™ increased the melanin synthesis by 19%.
a skin condition that causes de-pigmentation of sections of skin[28]. An agonist of α‐melanocyte‐stimulating hormone (α‐MSH), a biomimetic peptide (palmitoyl tetrapeptide‐20, PTP20) was developed by Scalvino et al. and was found to enhance hair pigmentation, and retard hair-greying process[29]. Redenhair in Spain has developed Greyverse, which is an α-MSH analogue capable of binding to MC1-R, a transmembrane receptor located on the surface of the melanocytes and causing stimulation of melanogenesis process. It reduces the accumulation of H2O2 responsible for accelerating the grey hair formation process[30]. Experimental results showed that only 0.5% of Greyverse™ increased the melanin synthesis by 19%. For natural and permanent reversal of grey hair, Reparex has introduced products that can restore the original colour of hair from the inside. Reparex removes the accumulated oxygen from the hair by using an enzyme called G-reductase, which binds to silver nitrate. This will restore the melanin’s natural colour over time[35].
For natural and permanent reversal of grey hair, Reparex has introduced products that can restore the original colour of hair from the inside. Reparex removes the accumulated oxygen from the hair by using an enzyme called G-reductase, which binds to silver nitrate. This will restore the melanin’s natural colour over time[35].
 People suffering from premature greying have a reduced level of copper in their blood serum which, in turn, reduces the activity of tyrosinase and hence, reduces pigment production. Based on this, scientists at Oxford Biolabs have developed Melaniq®, which includes copper, a necessary component of the biosynthesis of melanin[38].
People suffering from premature greying have a reduced level of copper in their blood serum which, in turn, reduces the activity of tyrosinase and hence, reduces pigment production. Based on this, scientists at Oxford Biolabs have developed Melaniq®, which includes copper, a necessary component of the biosynthesis of melanin[38].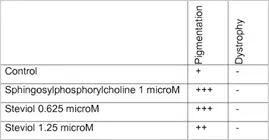 DSM has developed a patented salt of steviol or isosteviol for topical cosmetic and non-therapeutic use in hair for restoring hair color (
DSM has developed a patented salt of steviol or isosteviol for topical cosmetic and non-therapeutic use in hair for restoring hair color ( L’Oreal, in its patent
L’Oreal, in its patent  START-UP ACTIVITY
START-UP ACTIVITY